Angioplasty
Angioplasty is a medical procedure designed to widen narrowed arteries with plaque buildup. The process involves using a small balloon to compress the plaque against the artery walls, facilitating improved blood flow. In many cases, a stent or tube is additionally inserted into the newly expanded area to maintain its openness.
Overview
What is Angioplasty?
Angioplasty, also known as balloon angioplasty, is a minimally invasive procedure designed to open narrowed arteries, enhancing the flow of blood. This technique is employed in areas where the presence of plaque narrows or obstructs arterial pathways.
Who Needs Angioplasty?
Angioplasty is recommended for individuals with coronary artery disease or those who have experienced a heart attack. It is also utilized in other parts of the body with narrowed or blocked arteries, such as the neck, arms, legs, kidneys, and pelvis. The procedure facilitates improved blood supply to organs affected by narrowed or blocked arteries.
Conditions Treated by Angioplasty:
Angioplasty is effective in treating atherosclerosis, characterized by the accumulation of plaque composed of fat and cholesterol, in various parts of the body:
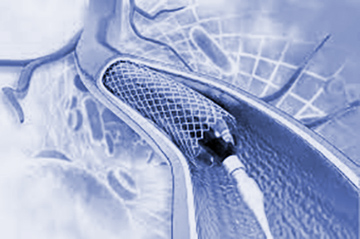
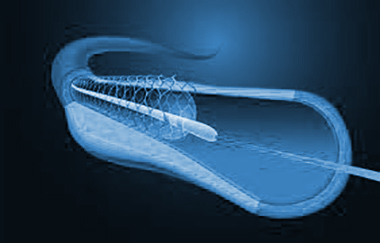
- Coronary Artery Disease: Coronary angioplasty, or percutaneous coronary intervention, addresses narrow or blocked coronary arteries, alleviating chest pain and preventing heart attacks.
- Peripheral Artery Disease: Angioplasty is utilized to treat atherosclerosis in major arteries of the arms, legs, and pelvis.
- Carotid Artery Disease: Angioplasty is beneficial for blocked arteries in the neck, reducing the risk of stroke by ensuring an adequate oxygen supply to the brain.
- Chronic Kidney Disease: Renal artery angioplasty may be performed when plaque accumulation affects kidney arteries, impacting oxygen delivery to the kidneys.
Procedure Details:
Before Angioplasty:
- - Patients are usually asked to abstain from eating or drinking for several hours before the procedure.
- - The duration of angioplasty varies but generally takes between half an hour to a few hours.
Preparation at the Hospital:
- - Upon arrival, patients wear a hospital gown and provide information on medications and allergies.
- - An IV is inserted for relaxing medication, and another medication to prevent blood clots is administered.
During Angioplasty:
- - A catheter is inserted through the skin into a blood vessel, guided by X-rays.
- - The cardiologist navigates the catheter to the blocked or narrowed coronary artery using contrast dye for visibility.
- - A wire and balloon catheter are introduced to move plaque aside, and a stent is often placed to keep the artery open.
- - Stents, with or without drug coatings, help prevent further narrowing.
Peripheral Artery Disease Variation:
- - For peripheral artery disease, a drug-coated balloon may be used to transfer medicine to the artery wall.
Patient Experience:
- - Some discomfort may be felt during balloon inflation, but it subsides upon deflation.
- - The balloon may be inflated multiple times if needed.
- - An angiogram compares blood flow before and after the procedure.
After Angioplasty:
- - Catheters are removed, and a bandage is applied to the insertion site.
- - Soreness or bruising may occur.
Risks / Benefits:
Advantages:
- - Lower risk and cost compared to surgical procedures.
- - Minimal wounds, typically one from catheters and a smaller one from the IV.
- - Stent placement is possible during angioplasty if needed.
Risks / Complications:
- - Complications are rare but may include emergency coronary artery bypass graft, reaction to dye, heart attack, abnormal heart rhythm, stroke, vessel or kidney damage, blood clots, chest pain, bleeding, and repeat blockage.
- - Complication risk is higher for older adults or those with multiple blocked arteries, kidney disease, or heart failure.
Recovery and Outlook:
Recovery Time:
- - Hospital stay is required for several hours or overnight.
- - Rest and fluid intake are recommended, and strenuous activity should be avoided for 24 hours.
Returning to Normal Activities:
- - Driving and work resumption typically after about a week for coronary angioplasty.
- - Follow provider's instructions regarding medications, including blood thinners.
When to Contact the Provider:
- - Follow-up visits are scheduled, but patients should contact their provider if experiencing bleeding, infection, color changes, pain, or warmth at catheter sites.
- - Any issues with prescribed anticlotting medications should be reported.
A Note on Lifestyle:
- - Emphasizes the importance of a healthy lifestyle post-angioplasty, including diet, exercise, and tobacco cessation.
- - Encourages adherence to prescribed medications and attendance at follow-up appointments.

