Coronary Revascularization
Revascularization encompasses a range of medical interventions aimed at restoring adequate blood flow to specific parts of the heart in cases where flow is restricted or blocked. These procedures include both surgical and minimally-invasive approaches. The primary goal is to address existing blood flow issues, particularly those associated with heart attacks, and some procedures also have a preventive aspect, reducing the risk of similar problems in the future.
Overview
Coronary revascularization is a set of medical procedures aimed at restoring blood flow to areas of the heart that suffer from inadequate blood supply. It encompasses both surgical and minimally-invasive interventions and is employed to address existing blood flow problems, particularly after a heart attack, and can serve as a preventive measure against future incidents.
Main Procedures:
Coronary revascularization typically involves two main procedures:
- Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI): A minimally-invasive procedure that restores blood flow from the inside.
- Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG): A surgical procedure where a bypass is created around a blocked artery.
Indications:
This treatment is relevant for individuals experiencing limited blood flow to parts of the heart, often associated with coronary artery disease. The frequency of revascularization procedures tends to be higher in individuals over 65, as coronary artery disease becomes more prevalent with age.
Purpose:
Coronary revascularization aims to address ischemia, a condition where cell damage occurs due to insufficient blood flow. Atherosclerosis, the accumulation of plaque in heart arteries, is a common cause. The procedures become crucial to prevent permanent damage or limit it by swiftly restoring blood flow.
Conditions Treated:
Coronary revascularization is applicable to various acute coronary syndrome conditions, including heart attacks, stable angina, and unstable angina.
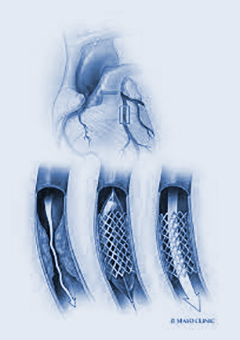
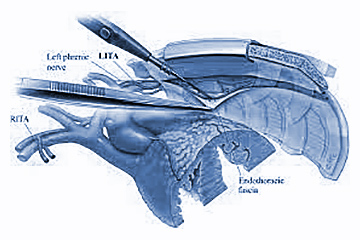
Procedure Details:
Before the Procedure:
- ● Diagnostic tests such as ECG, echocardiogram, and cardiac catheterization are conducted to plan the treatment.
- ● Fasting is typically required before the procedure, and an IV line is placed for fluid and medication administration.
- ● Sedative medication or general anesthesia may be administered based on the procedure type.
During the Procedure:
-
●
Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI):
- ○ A catheter is inserted through a major blood vessel, guided to the heart.
- ○ Tools such as balloon angioplasty and stenting may be utilized to restore blood flow.
- ○ Brachytherapy, involving internal radiation, may be employed.
-
●
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG):
- ○ Involves open surgery or minimally-invasive/robot-assisted surgery.
- ○ A blood vessel is harvested from the body, and the heart is accessed through chest incisions.
- ○ Bypass vessels are created to restore or maintain blood flow around blocked arteries.
- ○ Heart-lung bypass machine may be used during open surgery.
-
●
Specialized Approaches:
- ○ Total arterial revascularization involves using arteries, which may be more durable.
- ○ Transmyocardial revascularization (TMR) uses laser therapy to enhance blood flow and stimulate new vessel formation.
After the Procedure:
- ● Recovery time varies based on the procedure and individual health.
- ● Cardiac rehabilitation programs may be recommended for comprehensive recovery.
- ● Follow-up visits and testing are scheduled to monitor heart function.
- ● Adherence to healthcare provider's guidance on diet, physical activity, and medications is crucial.
Coronary revascularization is a vital intervention for individuals with compromised blood flow to the heart. Effective recovery involves a combination of medical procedures, rehabilitation, and ongoing monitoring to ensure the heart's optimal function and the patient's overall well-being. Asking questions and understanding post-procedural care are essential components of a successful recovery.
Coronary Revascularization: Risks, Benefits, and Recovery
Advantages:
- ● Preventive Ability: Coronary revascularization procedures are effective in preventing heart attacks, particularly when addressing coronary artery disease before a heart attack occurs.
- ● Life-Saving Potential: It serves as a crucial treatment for heart attacks, contributing to saving lives in emergency situations.
- ● Preservation of Heart Function: Swift coronary revascularization helps prevent or limit permanent damage to heart muscle cells caused by ischemia, the lack of blood flow.
Risks and Complications:
- ● PCI (Percutaneous Coronary Intervention): Risks involve potential damage to the heart or nearby blood vessels, leading to arrhythmias, blood clots, stroke, or bleeding.
- ● CABG (Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting): Surgery-related risks include pain, bleeding, and a risk of infection.
Overall Considerations:
- ● Risks and complications vary based on the specific procedure, as well as individual health factors such as age, existing conditions, and medical history.
- ● The healthcare provider is the best resource for providing personalized information on what to expect, including potential risks and complications.
Recovery and Outlook:
-
●
Recovery Time:
- ○ PCI generally has shorter recovery times, often as an outpatient procedure with a recovery period of days.
- ○ CABG involves a longer recovery, with a hospital stay of several days and an overall recovery duration of weeks to months.
-
●
Individualized Recovery:
- ○ The healthcare provider guides patients on the expected recovery duration and offers insights into the recovery process.
When to Seek Medical Attention:
- ● After a coronary revascularization procedure, patients should be vigilant for signs indicating potential issues. These symptoms include chest pain (angina), shortness of breath (dyspnea), dizziness, lightheadedness, fainting, or passing out.
- ● Early recognition and communication with healthcare providers can address concerns and ensure appropriate care.
A Note on Emotional Well-Being:
Acknowledges the emotional impact of heart-related concerns and highlights the importance of understanding coronary revascularization treatments. This understanding can help manage anxiety and enable individuals to focus on receiving necessary care and returning to a fulfilling life.

